5 tidy data 개념과 dplyr+tidyr로 데이터 다루기
데이터 분석을 어렵게 하는 여러 이유들이 있습니다. 이게 개발 커뮤니티에서 말하는 기술 부채와 같은 개념이지 않나 생각이 들어 데이터 부채라는 표현을 사용해 보았습니다. 여러 데이터 관련 구루들이 강조하는 바, 데이터 분석의 대부분의 시간(약 80%)은 데이터 수집과 전처리, 정제에 사용됩니다. 계륵 같은 일이죠. garbage in, garbage out; GIGO 이니까요. 데이터가 많지 않았던 시대에는 처리에 시간을 쏟는 것이 너무 당연한 일이었습니다. 하지만 데이터 생성을 설계할 수 있는 입장(서비스 제공자, 마케터 등)에서는 저 시간은 명확하게 비용, 즉 데이터 부채가 되는 것입니다.
이 데이터 부채가 쌓이는 것을 처음부터 막을 수 있도록 데이터가 저장되는 방식에 대해 제안된 개념이 있는데 그것이 tidy data입니다. tidy data란 개념은 Hadley Wickham이 제안했습니다.
5.1 단정한 데이터
이것에 대해 본인이 직접 장문의 설명을 한 것도 있고 R 한글 형태소 분석 패키지인 konlp을 만드신 고감자님의 한글 설명, MS의 데이터 과학자이시자 헬로우 데이터과학의 저자이신 김진영님의 도서 블로그에도 너무 잘 설명되어 있습니다. 추가로 더 내용이 필요하시면 참고하시기 바랍니다. 먼저 tidy data의 개념이 필요한 이유는 컴퓨터에게 분석을 시켜야(!) 하기 때문입니다. 그래서 tidy data는 사람이 눈으로 이해하기에는 적절하지 않을 수 있습니다. 이 곳이 진입장벽이 되기도 하는데, 현재 사용하고 있는 엑셀을 바로 R에 넣고 사용하고 싶은데, 잘 안되는 경우가 많습니다. 그것은 엑셀 파일내 데이터를 사람이 “보기 좋게” 위치했기 때문입니다. 그럼 이제 tidy data의 세 가지 조건을 원문(1)과 고감자님 번역(2), 김진영님 번역(3)순으로 살펴보겠습니다.
1.1 Each variable forms a column.
1.2 각 변수는 개별의 열(column)으로 존재한다.
1.3 각 열에는 개별 속성이 들어간다.
2.1 Each observation forms a row.
2.2 각 관측치는 행(row)를 구성한다.
2.3 각 행에는 개별 관찰 항목이 들어간다.
3.1 Each type of observational unit forms a table.
3.2 각 테이블은 단 하나의 관측기준에 의해서 조직된 데이터를 저장한다.
3.3 각 테이블에는 단일 유형의 데이터가 들어간다.

tidydata
1번을 보기 전에 2번을 먼저 보겠습니다.(2>1>3 순으로 쉬워요.) 2번은 단순합니다. 하나의 데이터가 한 줄(행)을 구성해야 한다는 것입니다. 설문지를 예로 들면 한명의 설문 결과가 한 줄로써 저장되는 것이죠. Each observation(개별 관찰)은 하나의 관찰 결과(=설문지 하나)를 뜻합니다. sql이나 data.frame에서 보셨듯 row는 조건으로 데이터를 filter할 수 있는 공간입니다. 그렇기 때문에 각 row는 개별 데이터를 의미합니다.
1번은 2번과 같은 하나가 들어가는 개념이긴 합니다만 하나의 variable, 변수, 개별 속성이라는 점이 조금 어렵습니다. 설문지 예시는 쉽습니다. 하나의 문항이라고 이해하면 되거든요. 그런데 variable이라는게 뭔지를 아는 것이 저는 조금 어려웠습니다. 찾아보니 영어상은 변수, 변할수 있는 수(여기서는 수보다는 값이라고 이해하시면 좋습니다.)인데 그 변수를 대표하는 이름이 컬럼명이라고 생각하면 좋더군요.
그런데 컬럼이 변수에 속하는 값으로 구성되는 경우가 있습니다. 예를들어 날짜가 컬럼명에 들어간 경우죠. 이렇게 생긴 데이터를 wide form이라고 합니다. 날짜는 변수에 들어갈 값이기 때문에 컬럼명을 날짜(date, datetime, when 등)로 정하고 컬럼에 속하는 cell에 날짜가 들어가는 형태로 구성하는 것이 tidy data의 조건을 충족하는 셈이 됩니다.
3번은 단일 테이블이 어떻게 구성되어야 하는지를 알려주는 조건입니다. 김진영님의 번역이 좀 이해하기 쉬운 것 같습니다. 테이블 하나에 하나의 데이터가 들어가야 된다는 뜻인데요, 아래 dplyr과 tidyr을 배우면서 예시들도 같이 보겠습니다.
5.2 dplyr + tidyr
dplyr은 plyr 패키지의 data.frame 전용이라는 의미를 가지고 있습니다. plyr은 데이터의 분해 - 적용 - 재조립 전략을 실행할 수 있는 패키지입니다. 이 전략을 data.frame 형태에서 실행하기 위해서 여러 명령어들을 제공합니다. 잘 정돈된 데이터 프레임은 분해 - 적용 - 재조립 전략을 실행하기 쉬우며 데이터를 잘 정돈하기 위해 tidyr 패키지를 함께 사용할 수 있습니다. 최근 ggplot2, dplyr, tidyr 등 tidy data의 개념과 같은 맥락에 있는 패키지들이 하나로 모여 tidyverse 패키지가 되었습니다.
library(tidyverse)
#> + ggplot2 2.2.1 Date: 2017-08-20
#> + tibble 1.3.3 R: 3.4.0
#> + tidyr 0.6.3 OS: Windows 10 x64
#> + readr 1.1.1 GUI: RTerm
#> + purrr 0.2.3 Locale: Korean_Korea.949
#> + dplyr 0.7.2 TZ: Asia/Seoul
#> + stringr 1.2.0
#> + forcats 0.2.0
#> Warning: 패키지 'ggplot2'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'tibble'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'tidyr'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'readr'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'purrr'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'dplyr'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'stringr'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> Warning: 패키지 'forcats'는 R 버전 3.4.1에서 작성되었습니다
#> ─ Conflicts ──────────────────────────
#> * filter(), from dplyr, masks stats::filter()
#> * lag(), from dplyr, masks stats::lag()5.2.1 pipe 연산자 %>%
%>%는 함수의 사용 방향을 바꿔서 읽고 이해하기 쉽게 만든 연산자입니다.
g(f(y)) == y %>% f() %>% g()이렇게 사용하고 tidyverse 패키지 전반적으로 사용하는 방식입니다.
.으로 앞의 변수의 위치를 지정할 수도 있고, 괄호 안에 작성할 것이 없을 때는 괄호를 생략할 수도 있습니다.
g(f(x,y,z)) == y %>% f(x, . , z) %>% g5.2.2 dplyr 명령어 소개
dplyr에는 행에 조건을 줘서 부분을 불러오는 filter(), 필요한 컬럼만 선택하는 select(), 새로운 컬럼을 계산하는 mutate(), 조건에 따라 재정렬 할 수 있는 arrange(), group_by()와 함께 써서 요약값을 계산할 수 있는 summarise()가 있습니다. group_by()는 mutate(), filter()와도 사용할 수 있습니다.
if(!require(nycflights13)) install.packages("nycflights13")
#> 필요한 패키지를 로딩중입니다: nycflights13
library(nycflights13)
flights
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>첫번째 filter()를 사용해 보겠습니다.
filter(flights, month == 1, day == 1)
#> # A tibble: 842 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 836 more rows, and 12 more variables: sched_arr_time <int>,
#> # arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
#> # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>,
#> # minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
jan1 <- filter(flights, month == 1, day == 1)
(dec25 <- filter(flights, month == 12, day == 25))
#> # A tibble: 719 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 12 25 456 500 -4 649
#> 2 2013 12 25 524 515 9 805
#> 3 2013 12 25 542 540 2 832
#> 4 2013 12 25 546 550 -4 1022
#> 5 2013 12 25 556 600 -4 730
#> 6 2013 12 25 557 600 -3 743
#> # ... with 713 more rows, and 12 more variables: sched_arr_time <int>,
#> # arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
#> # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>,
#> # minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>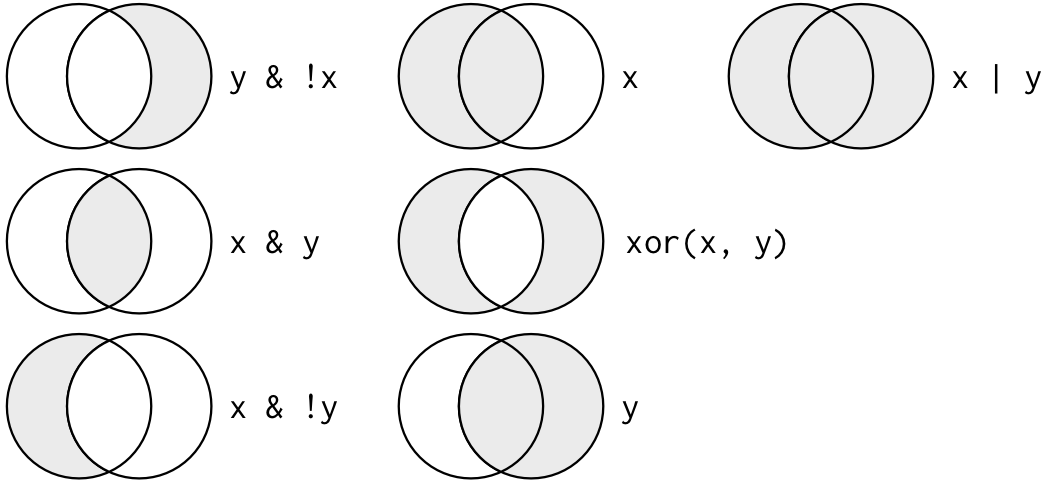
logical
filter(flights, month == 11 | month == 12)
#> # A tibble: 55,403 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 11 1 5 2359 6 352
#> 2 2013 11 1 35 2250 105 123
#> 3 2013 11 1 455 500 -5 641
#> 4 2013 11 1 539 545 -6 856
#> 5 2013 11 1 542 545 -3 831
#> 6 2013 11 1 549 600 -11 912
#> # ... with 5.54e+04 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
nov_dec <- filter(flights, month %in% c(11, 12))
nov_dec
#> # A tibble: 55,403 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 11 1 5 2359 6 352
#> 2 2013 11 1 35 2250 105 123
#> 3 2013 11 1 455 500 -5 641
#> 4 2013 11 1 539 545 -6 856
#> 5 2013 11 1 542 545 -3 831
#> 6 2013 11 1 549 600 -11 912
#> # ... with 5.54e+04 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
filter(flights, !(arr_delay > 120 | dep_delay > 120))
#> # A tibble: 316,050 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.16e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
filter(flights, arr_delay <= 120, dep_delay <= 120)
#> # A tibble: 316,050 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.16e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>arrange()는 조건을 바탕으로 정렬을 다시 해줍니다.
arrange(flights, year, month, day)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
arrange(flights, desc(arr_delay))
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 9 641 900 1301 1242
#> 2 2013 6 15 1432 1935 1137 1607
#> 3 2013 1 10 1121 1635 1126 1239
#> 4 2013 9 20 1139 1845 1014 1457
#> 5 2013 7 22 845 1600 1005 1044
#> 6 2013 4 10 1100 1900 960 1342
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
df <- tibble(x = c(5, 2, NA))
arrange(df, x)
#> # A tibble: 3 x 1
#> x
#> <dbl>
#> 1 2
#> 2 5
#> 3 NA
arrange(df, desc(x))
#> # A tibble: 3 x 1
#> x
#> <dbl>
#> 1 5
#> 2 2
#> 3 NAselect()는 컬럼을 선택하는 함수라고 했습니다.
select(flights, year, month, day)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 3
#> year month day
#> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1
#> 2 2013 1 1
#> 3 2013 1 1
#> 4 2013 1 1
#> 5 2013 1 1
#> 6 2013 1 1
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows
select(flights, year:day)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 3
#> year month day
#> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1
#> 2 2013 1 1
#> 3 2013 1 1
#> 4 2013 1 1
#> 5 2013 1 1
#> 6 2013 1 1
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows
select(flights, -(year:day))
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 16
#> dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time arr_delay
#> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 517 515 2 830 819 11
#> 2 533 529 4 850 830 20
#> 3 542 540 2 923 850 33
#> 4 544 545 -1 1004 1022 -18
#> 5 554 600 -6 812 837 -25
#> 6 554 558 -4 740 728 12
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 10 more variables: carrier <chr>,
#> # flight <int>, tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>select와 함께 사용하는 함수로 starts_with("abc"), ends_with("xyz"), contains("ijk"), matches("(.)\\1"), num_range("x", 1:3)등을 들 수 있습니다. ?select를 실행해서 자세한 사항을 확인해보세요.
rename()은 컬럼의 이름을 바꾸는 함수고, everything()은 선택한 것 이외에 전부를 뜻합니다.
rename(flights, tail_num = tailnum)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tail_num <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
select(flights, time_hour, air_time, everything())
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19
#> time_hour air_time year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
#> <dttm> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013-01-01 05:00:00 227 2013 1 1 517 515
#> 2 2013-01-01 05:00:00 227 2013 1 1 533 529
#> 3 2013-01-01 05:00:00 160 2013 1 1 542 540
#> 4 2013-01-01 05:00:00 183 2013 1 1 544 545
#> 5 2013-01-01 06:00:00 116 2013 1 1 554 600
#> 6 2013-01-01 05:00:00 150 2013 1 1 554 558
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables: dep_delay <dbl>,
#> # arr_time <int>, sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>,
#> # flight <int>, tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, distance <dbl>,
#> # hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>mutate()는 새로운 변수 계산을 위해서 필요합니다.
flights_sml <- select(flights,
year:day,
ends_with("delay"),
distance,
air_time
)
mutate(flights_sml,
gain = arr_delay - dep_delay,
speed = distance / air_time * 60
)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 9
#> year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time gain speed
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 227 9 370
#> 2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 227 16 374
#> 3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 160 31 408
#> 4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 183 -17 517
#> 5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 116 -19 394
#> 6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 150 16 288
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows
mutate(flights_sml,
gain = arr_delay - dep_delay,
hours = air_time / 60,
gain_per_hour = gain / hours
)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 10
#> year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time gain hours
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 227 9 3.78
#> 2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 227 16 3.78
#> 3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 160 31 2.67
#> 4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 183 -17 3.05
#> 5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 116 -19 1.93
#> 6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 150 16 2.50
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 1 more variables: gain_per_hour <dbl>
transmute(flights,
gain = arr_delay - dep_delay,
hours = air_time / 60,
gain_per_hour = gain / hours
)
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 3
#> gain hours gain_per_hour
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 9 3.78 2.38
#> 2 16 3.78 4.23
#> 3 31 2.67 11.62
#> 4 -17 3.05 -5.57
#> 5 -19 1.93 -9.83
#> 6 16 2.50 6.40
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows특별히 mutate()와 함께 사용하는 함수중에 lag()와 lead()를 소개할까 합니다.
(x <- 1:10)
#> [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
lag(x)
#> [1] NA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
lead(x)
#> [1] 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NAmutate()가 각 행에 대한 계산 결과를 하나의 컬럼으로 만들어 주는 것이라면 summarise()는 일정 조건(대부분 group_by()를 이용한 그룹화)에 해당하는 계산을 수행해줍니다.
summarise(flights, delay = mean(dep_delay, na.rm = TRUE))
#> # A tibble: 1 x 1
#> delay
#> <dbl>
#> 1 12.6
by_day <- group_by(flights, year, month, day)
summarise(by_day, delay = mean(dep_delay, na.rm = TRUE))
#> # A tibble: 365 x 4
#> # Groups: year, month [?]
#> year month day delay
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 11.55
#> 2 2013 1 2 13.86
#> 3 2013 1 3 10.99
#> 4 2013 1 4 8.95
#> 5 2013 1 5 5.73
#> 6 2013 1 6 7.15
#> # ... with 359 more rows
daily <- group_by(flights, year, month, day)
(per_day <- summarise(daily, flights = n()))
#> # A tibble: 365 x 4
#> # Groups: year, month [?]
#> year month day flights
#> <int> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 842
#> 2 2013 1 2 943
#> 3 2013 1 3 914
#> 4 2013 1 4 915
#> 5 2013 1 5 720
#> 6 2013 1 6 832
#> # ... with 359 more rows
(per_month <- summarise(per_day, flights = sum(flights)))
#> # A tibble: 12 x 3
#> # Groups: year [?]
#> year month flights
#> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 27004
#> 2 2013 2 24951
#> 3 2013 3 28834
#> 4 2013 4 28330
#> 5 2013 5 28796
#> 6 2013 6 28243
#> # ... with 6 more rows
(per_year <- summarise(per_month, flights = sum(flights)))
#> # A tibble: 1 x 2
#> year flights
#> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 336776
daily %>%
ungroup() %>%
summarise(flights = n())
#> # A tibble: 1 x 1
#> flights
#> <int>
#> 1 336776group_by()를 mutate(), filter()와도 사용할 수 있다고 했습니다.
flights_sml %>%
group_by(year, month, day) %>%
filter(rank(desc(arr_delay)) < 10)
#> # A tibble: 3,306 x 7
#> # Groups: year, month, day [365]
#> year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance air_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 853 851 184 41
#> 2 2013 1 1 290 338 1134 213
#> 3 2013 1 1 260 263 266 46
#> 4 2013 1 1 157 174 213 60
#> 5 2013 1 1 216 222 708 121
#> 6 2013 1 1 255 250 589 115
#> # ... with 3,300 more rows
popular_dests <- flights %>%
group_by(dest) %>%
filter(n() > 365)
popular_dests
#> # A tibble: 332,577 x 19
#> # Groups: dest [77]
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740
#> # ... with 3.326e+05 more rows, and 12 more variables:
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
#> # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
popular_dests %>%
filter(arr_delay > 0) %>%
mutate(prop_delay = arr_delay / sum(arr_delay)) %>%
select(year:day, dest, arr_delay, prop_delay)
#> # A tibble: 131,106 x 6
#> # Groups: dest [77]
#> year month day dest arr_delay prop_delay
#> <int> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 IAH 11 1.11e-04
#> 2 2013 1 1 IAH 20 2.01e-04
#> 3 2013 1 1 MIA 33 2.35e-04
#> 4 2013 1 1 ORD 12 4.24e-05
#> 5 2013 1 1 FLL 19 9.38e-05
#> 6 2013 1 1 ORD 8 2.83e-05
#> # ... with 1.311e+05 more rows5.2.3 tidyr 명령어 소개
tidyr에는 long form을 wide form으로 바꿔주는 spread(), 반대로 wide form을 long form으로 바꿔주는 gather(), 여러 의미를 지닌 데이터를 특정 글자를 기준으로 분리해 주는 seperate(), 그 반대로 합치는 unite(), 데이터를 분리하는 폼을 지정해 줄 수 있는 extract()가 있습니다.
우선 내장된 데이터를 소개하겠습니다.
table1
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> country year cases population
#> <chr> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258 1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766 1280428583
table2
#> # A tibble: 12 x 4
#> country year type count
#> <chr> <int> <chr> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 cases 745
#> 2 Afghanistan 1999 population 19987071
#> 3 Afghanistan 2000 cases 2666
#> 4 Afghanistan 2000 population 20595360
#> 5 Brazil 1999 cases 37737
#> 6 Brazil 1999 population 172006362
#> # ... with 6 more rows
table3
#> # A tibble: 6 x 3
#> country year rate
#> * <chr> <int> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745/19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666/20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737/172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488/174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258/1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766/1280428583
table4a
#> # A tibble: 3 x 3
#> country `1999` `2000`
#> * <chr> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 745 2666
#> 2 Brazil 37737 80488
#> 3 China 212258 213766
table4b
#> # A tibble: 3 x 3
#> country `1999` `2000`
#> * <chr> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 19987071 20595360
#> 2 Brazil 172006362 174504898
#> 3 China 1272915272 1280428583이제 많이 사용하게 될 gather() 함수를 보겠습니다.
table4a
#> # A tibble: 3 x 3
#> country `1999` `2000`
#> * <chr> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 745 2666
#> 2 Brazil 37737 80488
#> 3 China 212258 213766
table4a %>%
gather(`1999`, `2000`, key = "year", value = "cases")
#> # A tibble: 6 x 3
#> country year cases
#> <chr> <chr> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745
#> 2 Brazil 1999 37737
#> 3 China 1999 212258
#> 4 Afghanistan 2000 2666
#> 5 Brazil 2000 80488
#> 6 China 2000 213766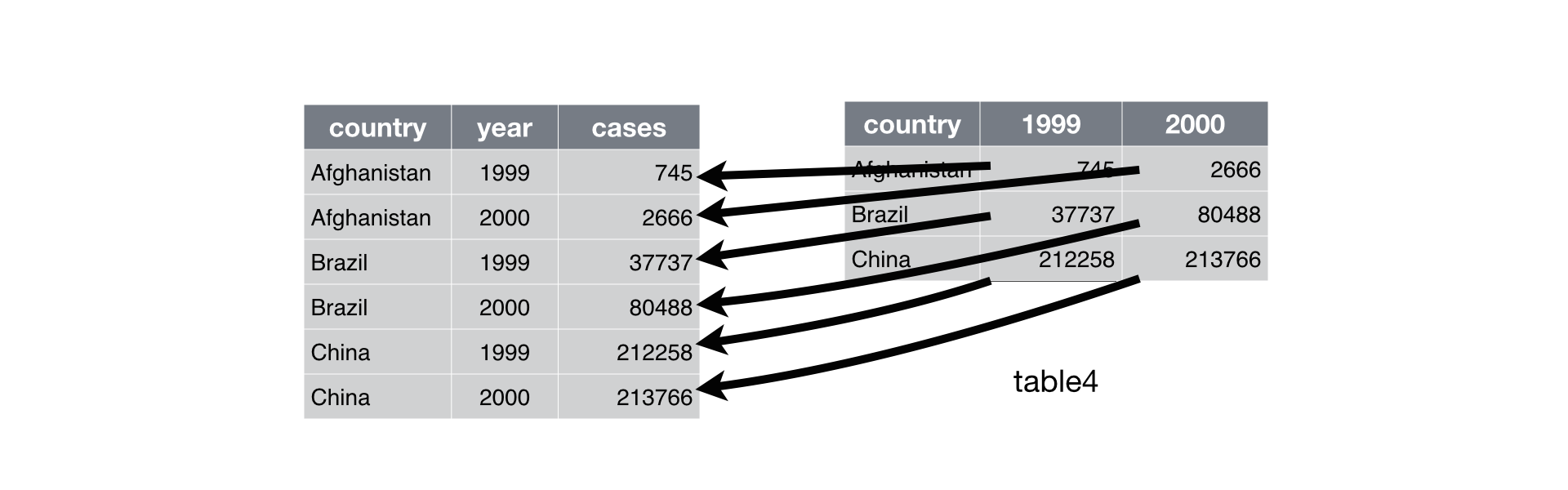
gather
이번엔 반대과정인 spread()를 보겠습니다.
table2
#> # A tibble: 12 x 4
#> country year type count
#> <chr> <int> <chr> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 cases 745
#> 2 Afghanistan 1999 population 19987071
#> 3 Afghanistan 2000 cases 2666
#> 4 Afghanistan 2000 population 20595360
#> 5 Brazil 1999 cases 37737
#> 6 Brazil 1999 population 172006362
#> # ... with 6 more rows
spread(table2, key = type, value = count)
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> country year cases population
#> * <chr> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258 1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766 1280428583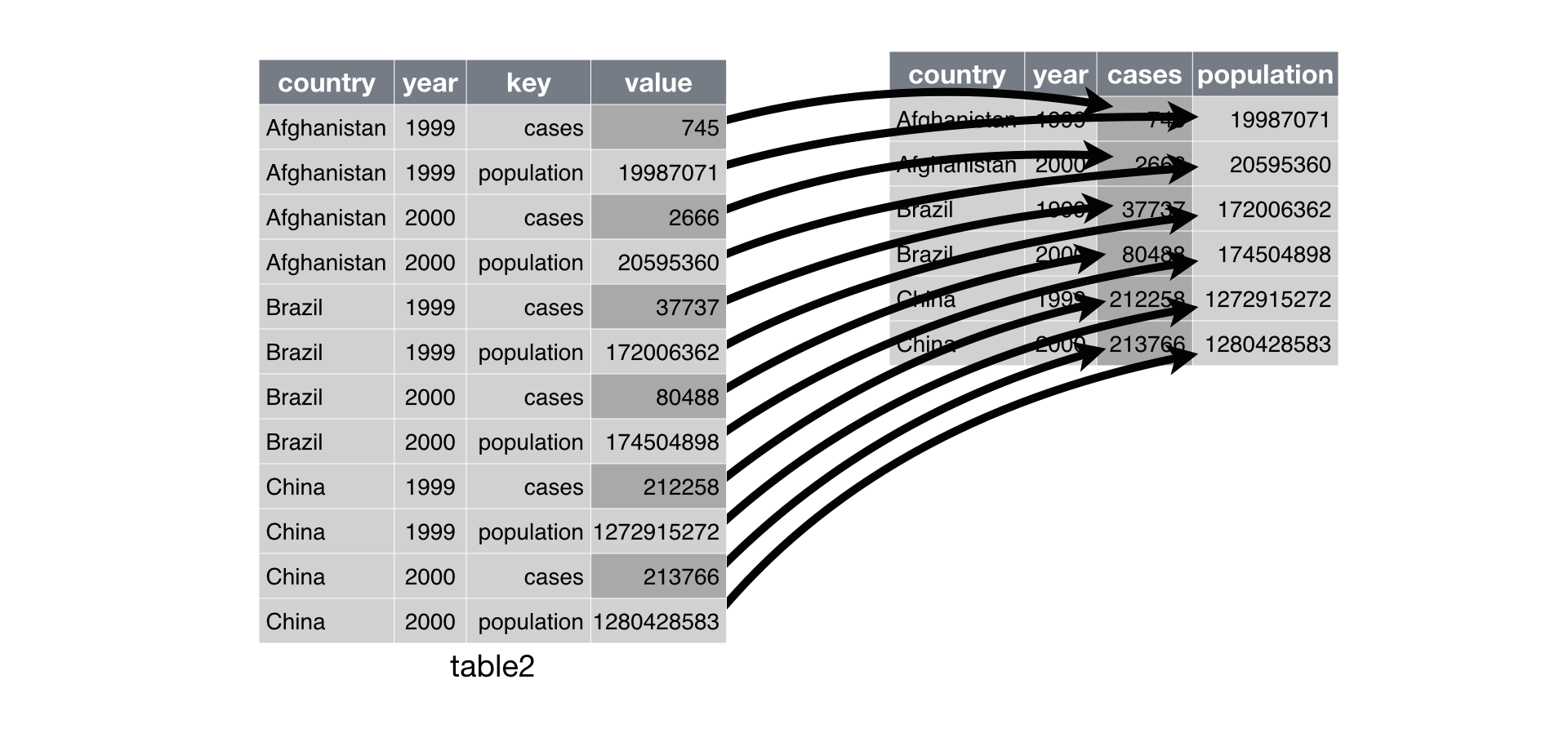
spread
한 셀에 여러 값이 있어서 나눠야 할 때는 seperate()를 사용합니다. sep옵션을 주지 않아도, 간단한 것은 알아서 나눠줍니다.
table3
#> # A tibble: 6 x 3
#> country year rate
#> * <chr> <int> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745/19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666/20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737/172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488/174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258/1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766/1280428583
table3 %>%
separate(rate, into = c("cases", "population"))
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> country year cases population
#> * <chr> <int> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258 1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766 1280428583
table3 %>%
separate(rate, into = c("cases", "population"), convert = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> country year cases population
#> * <chr> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258 1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766 1280428583
table3 %>%
separate(year, into = c("century", "year"), sep = 2)
#> # A tibble: 6 x 4
#> country century year rate
#> * <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 19 99 745/19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 20 00 2666/20595360
#> 3 Brazil 19 99 37737/172006362
#> 4 Brazil 20 00 80488/174504898
#> 5 China 19 99 212258/1272915272
#> 6 China 20 00 213766/1280428583unite()는 합쳐주는 seperate()와는 반대의 기능을 가진 함수입니다.
table5 %>%
unite(new, century, year)
#> # A tibble: 6 x 3
#> country new rate
#> * <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 19_99 745/19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 20_00 2666/20595360
#> 3 Brazil 19_99 37737/172006362
#> 4 Brazil 20_00 80488/174504898
#> 5 China 19_99 212258/1272915272
#> 6 China 20_00 213766/1280428583
table5 %>%
unite(new, century, year, sep = "")
#> # A tibble: 6 x 3
#> country new rate
#> * <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Afghanistan 1999 745/19987071
#> 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666/20595360
#> 3 Brazil 1999 37737/172006362
#> 4 Brazil 2000 80488/174504898
#> 5 China 1999 212258/1272915272
#> 6 China 2000 213766/12804285835.2.4 dplyr과 join {#dplyr&join}
dplyr에는 join() 기능도 있습니다. 데이터를 먼저 소개하겠습니다.
airlines
#> # A tibble: 16 x 2
#> carrier name
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 9E Endeavor Air Inc.
#> 2 AA American Airlines Inc.
#> 3 AS Alaska Airlines Inc.
#> 4 B6 JetBlue Airways
#> 5 DL Delta Air Lines Inc.
#> 6 EV ExpressJet Airlines Inc.
#> # ... with 10 more rows
airports
#> # A tibble: 1,458 x 8
#> faa name lat lon alt tz dst
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 04G Lansdowne Airport 41.1 -80.6 1044 -5 A
#> 2 06A Moton Field Municipal Airport 32.5 -85.7 264 -6 A
#> 3 06C Schaumburg Regional 42.0 -88.1 801 -6 A
#> 4 06N Randall Airport 41.4 -74.4 523 -5 A
#> 5 09J Jekyll Island Airport 31.1 -81.4 11 -5 A
#> 6 0A9 Elizabethton Municipal Airport 36.4 -82.2 1593 -5 A
#> # ... with 1,452 more rows, and 1 more variables: tzone <chr>
planes
#> # A tibble: 3,322 x 9
#> tailnum year type manufacturer model engines
#> <chr> <int> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int>
#> 1 N10156 2004 Fixed wing multi engine EMBRAER EMB-145XR 2
#> 2 N102UW 1998 Fixed wing multi engine AIRBUS INDUSTRIE A320-214 2
#> 3 N103US 1999 Fixed wing multi engine AIRBUS INDUSTRIE A320-214 2
#> 4 N104UW 1999 Fixed wing multi engine AIRBUS INDUSTRIE A320-214 2
#> 5 N10575 2002 Fixed wing multi engine EMBRAER EMB-145LR 2
#> 6 N105UW 1999 Fixed wing multi engine AIRBUS INDUSTRIE A320-214 2
#> # ... with 3,316 more rows, and 3 more variables: seats <int>,
#> # speed <int>, engine <chr>
weather
#> # A tibble: 26,130 x 15
#> origin year month day hour temp dewp humid wind_dir wind_speed
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 EWR 2013 1 1 0 37.0 21.9 54.0 230 10.4
#> 2 EWR 2013 1 1 1 37.0 21.9 54.0 230 13.8
#> 3 EWR 2013 1 1 2 37.9 21.9 52.1 230 12.7
#> 4 EWR 2013 1 1 3 37.9 23.0 54.5 230 13.8
#> 5 EWR 2013 1 1 4 37.9 24.1 57.0 240 15.0
#> 6 EWR 2013 1 1 6 39.0 26.1 59.4 270 10.4
#> # ... with 2.612e+04 more rows, and 5 more variables: wind_gust <dbl>,
#> # precip <dbl>, pressure <dbl>, visib <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>%>%와 join() 명령어로 쉽게 데이터를 합칠 수 있습니다.
flights2 <- flights %>%
select(year:day, hour, origin, dest, tailnum, carrier)
flights2
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 8
#> year month day hour origin dest tailnum carrier
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 EWR IAH N14228 UA
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 LGA IAH N24211 UA
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 JFK MIA N619AA AA
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 JFK BQN N804JB B6
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 LGA ATL N668DN DL
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 EWR ORD N39463 UA
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows
flights2 %>%
select(-origin, -dest) %>%
left_join(airlines, by = "carrier")
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 7
#> year month day hour tailnum carrier name
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 N14228 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 N24211 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 N619AA AA American Airlines Inc.
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 N804JB B6 JetBlue Airways
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 N668DN DL Delta Air Lines Inc.
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 N39463 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows
flights2 %>%
select(-origin, -dest) %>%
mutate(name = airlines$name[match(carrier, airlines$carrier)])
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 7
#> year month day hour tailnum carrier name
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 N14228 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 N24211 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 N619AA AA American Airlines Inc.
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 N804JB B6 JetBlue Airways
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 N668DN DL Delta Air Lines Inc.
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 N39463 UA United Air Lines Inc.
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rowskey를 선정해주는 것과 아닌 것이 어떻게 다른지 봐주세요.
flights2 %>%
left_join(weather)
#> Joining, by = c("year", "month", "day", "hour", "origin")
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 18
#> year month day hour origin dest tailnum carrier temp dewp humid
#> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 EWR IAH N14228 UA NA NA NA
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 LGA IAH N24211 UA NA NA NA
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 JFK MIA N619AA AA NA NA NA
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 JFK BQN N804JB B6 NA NA NA
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 LGA ATL N668DN DL 39.9 26.1 57.3
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 EWR ORD N39463 UA NA NA NA
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 7 more variables: wind_dir <dbl>,
#> # wind_speed <dbl>, wind_gust <dbl>, precip <dbl>, pressure <dbl>,
#> # visib <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
flights2 %>%
left_join(planes, by = "tailnum")
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 16
#> year.x month day hour origin dest tailnum carrier year.y
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 EWR IAH N14228 UA 1999
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 LGA IAH N24211 UA 1998
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 JFK MIA N619AA AA 1990
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 JFK BQN N804JB B6 2012
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 LGA ATL N668DN DL 1991
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 EWR ORD N39463 UA 2012
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 7 more variables: type <chr>,
#> # manufacturer <chr>, model <chr>, engines <int>, seats <int>,
#> # speed <int>, engine <chr>왼쪽 테이블과 오른쪽 테이블의 어떤 key를 기준으로 join()할 건지 지정할 수 있습니다.
flights2 %>%
left_join(airports, c("dest" = "faa"))
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 15
#> year month day hour origin dest tailnum carrier
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 EWR IAH N14228 UA
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 LGA IAH N24211 UA
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 JFK MIA N619AA AA
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 JFK BQN N804JB B6
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 LGA ATL N668DN DL
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 EWR ORD N39463 UA
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 7 more variables: name <chr>,
#> # lat <dbl>, lon <dbl>, alt <int>, tz <dbl>, dst <chr>, tzone <chr>
flights2 %>%
left_join(airports, c("origin" = "faa"))
#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 15
#> year month day hour origin dest tailnum carrier name
#> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 5 EWR IAH N14228 UA Newark Liberty Intl
#> 2 2013 1 1 5 LGA IAH N24211 UA La Guardia
#> 3 2013 1 1 5 JFK MIA N619AA AA John F Kennedy Intl
#> 4 2013 1 1 5 JFK BQN N804JB B6 John F Kennedy Intl
#> 5 2013 1 1 6 LGA ATL N668DN DL La Guardia
#> 6 2013 1 1 5 EWR ORD N39463 UA Newark Liberty Intl
#> # ... with 3.368e+05 more rows, and 6 more variables: lat <dbl>,
#> # lon <dbl>, alt <int>, tz <dbl>, dst <chr>, tzone <chr>join() 함수는 base::merge(), SQL과 비교할 수 있습니다.
inner_join(x, y) == merge(x, y)
left_join(x, y) == merge(x, y, all.x = TRUE)
right_join(x, y) == merge(x, y, all.y = TRUE),
full_join(x, y) == merge(x, y, all.x = TRUE, all.y = TRUE)
inner_join(x, y, by = "z") == SELECT * FROM x INNER JOIN y ON x.z = y.z
left_join(x, y, by = "z") == SELECT * FROM x LEFT OUTER JOIN y ON x.z = y.z
right_join(x, y, by = "z") == SELECT * FROM x RIGHT OUTER JOIN y ON x.z = y.z
full_join(x, y, by = "z") == SELECT * FROM x FULL OUTER JOIN y ON x.z = y.z5.2.5 dplyr과 SQL
dplyr은 데이터베이스에게 SQL 쿼리를 사용하는 것처럼 사용할 수 있습니다. 이곳에 잘 설명되어 있으니 참고하시기 바랍니다.
library(dplyr)
library(RSQLite)
library(RMySQL)
#> 필요한 패키지를 로딩중입니다: DBI
#> 필요한 패키지를 로딩중입니다: methods
#>
#> 다음의 패키지를 부착합니다: 'RMySQL'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:RSQLite':
#>
#> isIdCurrent
sqlite_db = src_sqlite('sqlite_db.sqlite3', create = T)
copy_to(sqlite_db, mtcars)
src_tbls(sqlite_db)
#> [1] "mtcars" "sqlite_stat1" "sqlite_stat4"
tbl(sqlite_db, 'mtcars')
#> # Source: table<mtcars> [?? x 11]
#> # Database: sqlite 3.19.3
#> # [C:\Users\mrchypark\Documents\project\data_camp_dabrp\sqlite_db.sqlite3]
#> mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.62 16.5 0 1 4 4
#> 2 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.88 17.0 0 1 4 4
#> 3 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4 1
#> 4 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.21 19.4 1 0 3 1
#> 5 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.44 17.0 0 0 3 2
#> 6 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.46 20.2 1 0 3 1
#> # ... with more rows
tbl(sqlite_db, sql('SELECT * FROM mtcars'))
#> # Source: SQL [?? x 11]
#> # Database: sqlite 3.19.3
#> # [C:\Users\mrchypark\Documents\project\data_camp_dabrp\sqlite_db.sqlite3]
#> mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.62 16.5 0 1 4 4
#> 2 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.88 17.0 0 1 4 4
#> 3 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4 1
#> 4 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.21 19.4 1 0 3 1
#> 5 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.44 17.0 0 0 3 2
#> 6 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.46 20.2 1 0 3 1
#> # ... with more rows
iris_db = tbl(sqlite_db, 'mtcars')
iris_db %>% filter(mpg > 20)
#> # Source: lazy query [?? x 11]
#> # Database: sqlite 3.19.3
#> # [C:\Users\mrchypark\Documents\project\data_camp_dabrp\sqlite_db.sqlite3]
#> mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.62 16.5 0 1 4 4
#> 2 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.88 17.0 0 1 4 4
#> 3 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4 1
#> 4 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.21 19.4 1 0 3 1
#> 5 24.4 4 147 62 3.69 3.19 20.0 1 0 4 2
#> 6 22.8 4 141 95 3.92 3.15 22.9 1 0 4 2
#> # ... with more rowssql_db = src_mysql(dbname="bank",user = "root",password = "XXXXX")
sql_db5.3 data.table
data.table은 지금까지와는 조금 다른 문법을 가지고 있습니다. fread와 fwrite이라는 강력한 IO함수를 가지고 있으며 data.table은 패키지 명이면서 data.frame과 호환되는 자료형이기도 합니다. 자세한 내용은 여기를 참고해 주세요.
library(data.table)
#>
#> 다음의 패키지를 부착합니다: 'data.table'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:dplyr':
#>
#> between, first, last
#> The following object is masked from 'package:purrr':
#>
#> transpose
url<-"https://github.com/arunsrinivasan/flights/wiki/NYCflights14/flights14.csv"
dir.create("./data",showWarnings = F)
download.file(url,destfile = "./data/flights14.csv")
system.time(flights <- read.csv("./data/flights14.csv"))
#> 사용자 시스템 elapsed
#> 5.04 0.16 5.92
system.time(flights <- fread("./data/flights14.csv"))
#> 사용자 시스템 elapsed
#> 0.30 0.03 0.34
flights
#> year month day dep_time dep_delay arr_time arr_delay cancelled
#> 1: 2014 1 1 914 14 1238 13 0
#> 2: 2014 1 1 1157 -3 1523 13 0
#> 3: 2014 1 1 1902 2 2224 9 0
#> 4: 2014 1 1 722 -8 1014 -26 0
#> 5: 2014 1 1 1347 2 1706 1 0
#> ---
#> 253312: 2014 10 31 1459 1 1747 -30 0
#> 253313: 2014 10 31 854 -5 1147 -14 0
#> 253314: 2014 10 31 1102 -8 1311 16 0
#> 253315: 2014 10 31 1106 -4 1325 15 0
#> 253316: 2014 10 31 824 -5 1045 1 0
#> carrier tailnum flight origin dest air_time distance hour min
#> 1: AA N338AA 1 JFK LAX 359 2475 9 14
#> 2: AA N335AA 3 JFK LAX 363 2475 11 57
#> 3: AA N327AA 21 JFK LAX 351 2475 19 2
#> 4: AA N3EHAA 29 LGA PBI 157 1035 7 22
#> 5: AA N319AA 117 JFK LAX 350 2475 13 47
#> ---
#> 253312: UA N23708 1744 LGA IAH 201 1416 14 59
#> 253313: UA N33132 1758 EWR IAH 189 1400 8 54
#> 253314: MQ N827MQ 3591 LGA RDU 83 431 11 2
#> 253315: MQ N511MQ 3592 LGA DTW 75 502 11 6
#> 253316: MQ N813MQ 3599 LGA SDF 110 659 8 24
dim(flights)
#> [1] 253316 17
ans <- flights[origin == "JFK" & month == 6L]
head(ans)
#> year month day dep_time dep_delay arr_time arr_delay cancelled carrier
#> 1: 2014 6 1 851 -9 1205 -5 0 AA
#> 2: 2014 6 1 1220 -10 1522 -13 0 AA
#> 3: 2014 6 1 718 18 1014 -1 0 AA
#> 4: 2014 6 1 1024 -6 1314 -16 0 AA
#> 5: 2014 6 1 1841 -4 2125 -45 0 AA
#> 6: 2014 6 1 1454 -6 1757 -23 0 AA
#> tailnum flight origin dest air_time distance hour min
#> 1: N787AA 1 JFK LAX 324 2475 8 51
#> 2: N795AA 3 JFK LAX 329 2475 12 20
#> 3: N784AA 9 JFK LAX 326 2475 7 18
#> 4: N791AA 19 JFK LAX 320 2475 10 24
#> 5: N790AA 21 JFK LAX 326 2475 18 41
#> 6: N785AA 117 JFK LAX 329 2475 14 54
ans <- flights[1:2]
ans
#> year month day dep_time dep_delay arr_time arr_delay cancelled carrier
#> 1: 2014 1 1 914 14 1238 13 0 AA
#> 2: 2014 1 1 1157 -3 1523 13 0 AA
#> tailnum flight origin dest air_time distance hour min
#> 1: N338AA 1 JFK LAX 359 2475 9 14
#> 2: N335AA 3 JFK LAX 363 2475 11 57
ans <- flights[order(origin, -dest)]
head(ans)
#> year month day dep_time dep_delay arr_time arr_delay cancelled carrier
#> 1: 2014 1 5 836 6 1151 49 0 EV
#> 2: 2014 1 6 833 7 1111 13 0 EV
#> 3: 2014 1 7 811 -6 1035 -13 0 EV
#> 4: 2014 1 8 810 -7 1036 -12 0 EV
#> 5: 2014 1 9 833 16 1055 7 0 EV
#> 6: 2014 1 13 923 66 1154 66 0 EV
#> tailnum flight origin dest air_time distance hour min
#> 1: N12175 4419 EWR XNA 195 1131 8 36
#> 2: N24128 4419 EWR XNA 190 1131 8 33
#> 3: N12142 4419 EWR XNA 179 1131 8 11
#> 4: N11193 4419 EWR XNA 184 1131 8 10
#> 5: N14198 4419 EWR XNA 181 1131 8 33
#> 6: N12157 4419 EWR XNA 188 1131 9 23
ans <- flights[, arr_delay]
head(ans)
#> [1] 13 13 9 -26 1 0
ans <- flights[, .(arr_delay, dep_delay)]
head(ans)
#> arr_delay dep_delay
#> 1: 13 14
#> 2: 13 -3
#> 3: 9 2
#> 4: -26 -8
#> 5: 1 2
#> 6: 0 4
ans <- flights[, .(delay_arr = arr_delay, delay_dep = dep_delay)]
head(ans)
#> delay_arr delay_dep
#> 1: 13 14
#> 2: 13 -3
#> 3: 9 2
#> 4: -26 -8
#> 5: 1 2
#> 6: 0 4
flights[, sum((arr_delay + dep_delay) < 0)]
#> [1] 141814
flights[origin == "JFK" & month == 6L,
.(m_arr = mean(arr_delay), m_dep = mean(dep_delay))]
#> m_arr m_dep
#> 1: 5.84 9.81
flights[origin == "JFK" & month == 6L, length(dest)]
#> [1] 8422
flights[, .(.N), by = .(origin)]
#> origin N
#> 1: JFK 81483
#> 2: LGA 84433
#> 3: EWR 87400
flights[carrier == "AA", .N, by = origin]
#> origin N
#> 1: JFK 11923
#> 2: LGA 11730
#> 3: EWR 2649
flights[carrier == "AA", .N, by = .(origin,dest)]
#> origin dest N
#> 1: JFK LAX 3387
#> 2: LGA PBI 245
#> 3: EWR LAX 62
#> 4: JFK MIA 1876
#> 5: JFK SEA 298
#> 6: EWR MIA 848
#> 7: JFK SFO 1312
#> 8: JFK BOS 1173
#> 9: JFK ORD 432
#> 10: JFK IAH 7
#> 11: JFK AUS 297
#> 12: EWR DFW 1618
#> 13: LGA ORD 4366
#> 14: JFK STT 229
#> 15: JFK SJU 690
#> 16: LGA MIA 3334
#> 17: LGA DFW 3785
#> 18: JFK LAS 595
#> 19: JFK MCO 597
#> 20: JFK EGE 85
#> 21: JFK DFW 474
#> 22: JFK SAN 299
#> 23: JFK DCA 172
#> 24: EWR PHX 121
#> origin dest N
flights[carrier == "AA", .N, by = .(origin, dest)][order(origin, -dest)][1:10,]
#> origin dest N
#> 1: EWR PHX 121
#> 2: EWR MIA 848
#> 3: EWR LAX 62
#> 4: EWR DFW 1618
#> 5: JFK STT 229
#> 6: JFK SJU 690
#> 7: JFK SFO 1312
#> 8: JFK SEA 298
#> 9: JFK SAN 299
#> 10: JFK ORD 432